TACMT: text-aware cross-modal transformer for visual grounding on high-resolution SAR images
作者:SunTianyang Li, Chao Wang, Sirui Tian, Bo Zhang, Fan Wu, Yixian Tang, Hong Zhang
论文链接:
论文代码:
发表时间:2025.02.24
摘要:
This paper introduces a novel task of visual grounding for high-resolution synthetic aperture radar images (SARVG). SARVG aims to identify the referred object in images through natural language instructions. While object detection on SAR images has been extensively investigated, identifying objects based on natural language remains under-explored. Due to the unique satellite view and side-look geometry, substantial expertise is often required to interpret objects, making it challenging to generalize across different sensors. Therefore, we propose to construct a dataset and develop multimodal deep learning models for the SARVG task. Our contributions can be summarized as follows. Using power transmission tower detection as an example, we have built a new benchmark of SARVG based on images from different SAR sensors to fully promote SARVG research. Subsequently, a novel text-aware cross-modal Transformer (TACMT) is proposed which follows DETR’s architecture. We develop a cross-modal encoder to enhance the visual features associated with the textual descriptions. Next, a text-aware query selection module is devised to select relevant context features as the decoder query. To retrieve the object from various scenes, we further design a cross-scale fusion module to fuse features from different levels for accurate target localization. Finally, extensive experiments on our dataset and widely used public datasets have demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed model. This work provides valuable insights for SAR image interpretation. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/CAESAR-Radi/TACMT.
1. 简介
SAR视觉定位(SARVG)——未完成
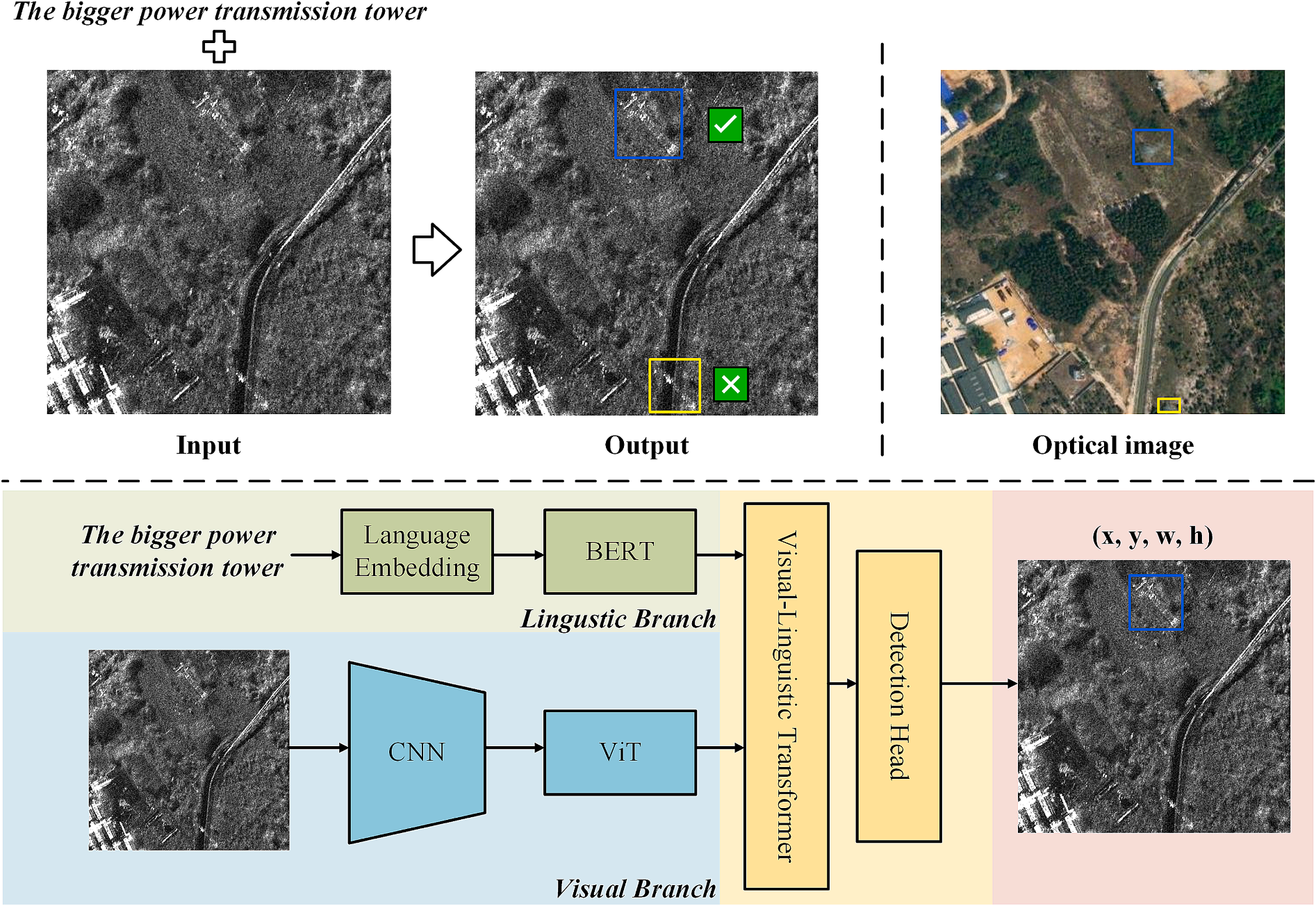
Fig. 1. SARVG示例和基本方法。第一行:输入图像-文本对,输出指定目标的边界框。第二行:基于端到端Transformer框架的经典视觉定位方法,该框架包含四个组件:语言分支、视觉分支、跨模态编码器和回归解码器。
2. 创新
提出跨模态文本感知Transformer(Text-Aware Cross-Modal Transformer,TACMT)。
构建基准数据集SARVG1.0,包含7617对图像-文本数据和2465张SAR图像切片。
使用跨模态编码器(Cross-Modal Encoder)和文本感知查询选择(Text-Aware Query Selection)模块进行不同阶段的视觉-文本特征融合。
提出高效的跨尺度融合(Cross-Scale Fusion)模块,通过学习不同尺度的视觉表征来提高SAR多尺度目标和复杂背景下视觉定位的精度。
3. 方法
3.1 流程
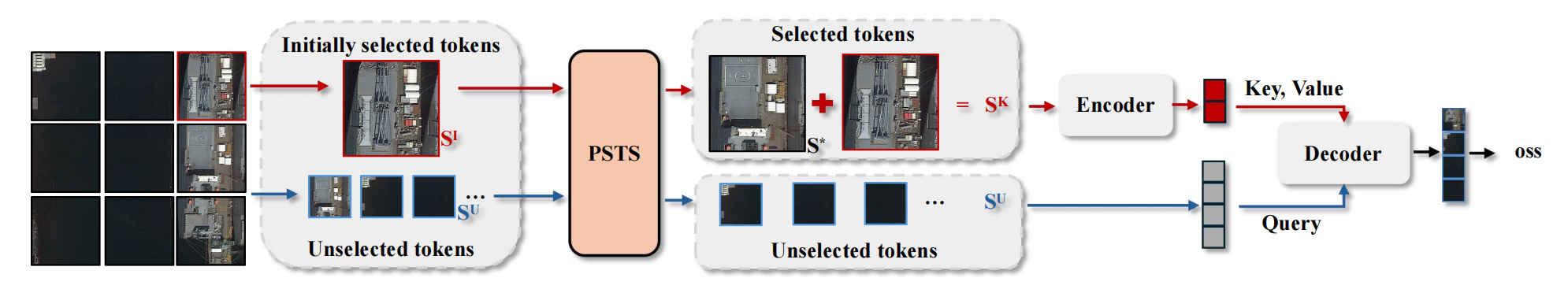
Fig. 2. 整体网络架构。在语言分支中,输入文本由预训练的自然语言模型(如BERT)进行处理。视觉分支提取并整合多级图像特征,具体而言,仅利用最后三个阶段(S3、S4、S5)的特征。为了降低复杂度,Transformer仅对最后一层特征进行编码。然后,文本和图像特征都被输入到跨模态编码器中,以增强所指对象的特征。最后,我们使用文本信息和增强的视觉特征来初始化对象查询,并使用检测头迭代更新边界框坐标。
3.2 跨模态编码器
3.2.1 问题
视觉特征图中不包含目标先验知识。
3.2.2 公式
F_{vf}=\mathrm{Flatten}(F_v),\mathbb{R}^{C \times d \times H \times W} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{C \times d \times N},N=H \times W。
F_g=\mathrm{MHA}(F_{vf},F_l,F_l)。
C=\exp (-1 \cdot \alpha (F^{'}_{vf}-F^{'}_g)),\alpha可学习。
F_{vc}=\mathrm{MHA}(F_g,F_g,F_{vf})。
F_{vl}=C \cdot (F_{vf}+F_{vc})。
3.2.3 流程
展开视觉特征图 F_v,得到 F_{vf}。
将 F_{vf} 作为查询Q、F_l 作为键K和值V,输入到多头自注意力(Multi-Head Self-Attention,\mathrm{MHA})中,得到相关的语义特征 F_g。
对 F_{vf} 和 F_g 使用线性投影(Linear Projection)和L1正则化(L1 Normalization),得到 F^{'}_{vf} 和 F^{'}_g。
使用 F^{'}_{vf} 和 F^{'}_g 计算两个模态的融合系数C。
使用 F_g 作为查询和键、F_{vf} 作为值,输入到 \mathrm{MHA},得到视觉和语言表征的特征相关性 F_{vc}。
最后,使用 F_{vf}、F_{vc}和C计算得到视觉-语言特征 F_{vl}。
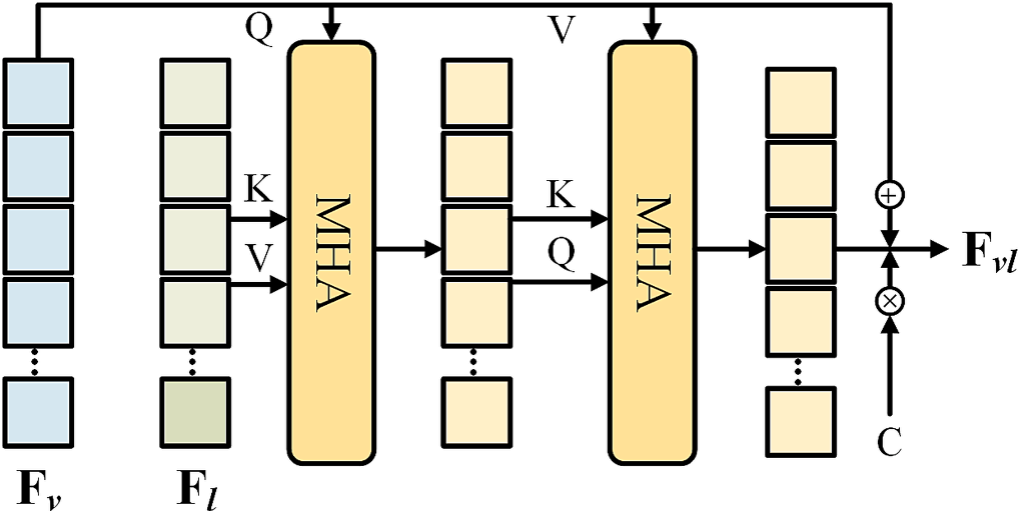
Fig. 3. 跨模态融合模块工作流程。在视觉、语言两种模态间引入协同注意力机制(Co-Attention),以获得调制(融合)的视觉特征。
3.3 文本感知查询选择模块
3.3.1 问题
目标查询的随机初始化导致类似 DETR的方法存在收敛缓慢和优化问题,且基于Transformer的检测器中的可学习嵌入(Embedding)缺乏明确的物理意义。
3.3.2 公式
b、i、t和c分别代表batch size、图像特征维度、文本特征维度和通道数,num被设置为1。
\mathrm{logits}_{b,i,t}=\sum_c \mathrm{image}_{b,i,c} \cdot \mathrm{text}_{b,t,c}。
\mathrm{index}_{b,i}=TopK(\max_t(\mathrm{logits}_{b,i,t}),\mathrm{num})。
3.3.3 流程
使用 \mathrm{image}_{b,i,c} 和 \mathrm{text}_{b,t,c} 计算对应的 \mathrm{logits}_{b,i,t}。
选择前num大的文本维度的 \mathrm{logits}_{b,i,t} 对应的 \mathrm{index}_{b,i}。
此外,在将文本信息输入进解码器前,将其与查询相合并(增强查询初始化可解释性)。
3.4 跨尺度融合模块
3.4.1 问题
高层特征包含丰富的语义信息,而缺乏位置信息;低层特征拥有更强的位置信息,但语义信息稀疏。
3.4.2 公式
x=Concat(F^i_v,F^j_v)。
F^{'}_v=\mathrm{Conv}_{1 \times 1}(\mathrm{Conv}_{1 \times 1}(x)+RepConv(\mathrm{Conv}_{1 \times 1}(x)))。
3.4.3 流程
自顶向下:使用 1 \times 1 卷积和最近邻插值法调整通道数和特征图大小。
自底向上:使用 3 \times 3 卷积调整通道数。
Fusion块:采用RepConv块 对相邻尺度的特征图进行融合。
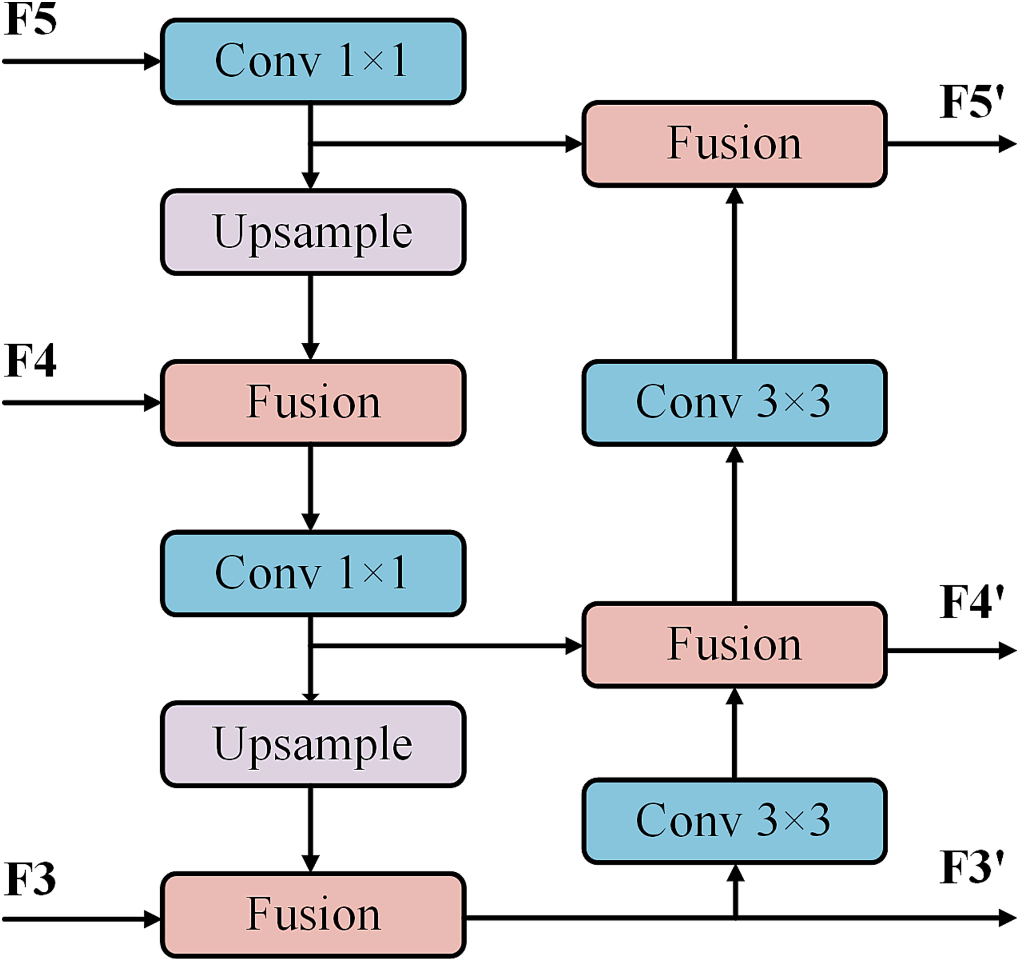
Fig. 4. 跨尺度融合模块。双向金字塔结构,整合低层位置信息和高层语义信息。
3.5 训练损失
3.5.1 问题
由于图像-文本通常是一对一,通过直接回归特定边界框,避免正负样本的分配。
3.5.2 公式
\lambda_{L1} 和 \lambda_{giou} 是用于调整两个损失之比的超参数。
L=\sum^{Num}_{i=1}\lambda_{L1} \mathscr{L}_{L1}(b^{gt},\hat{b}^i)+\lambda_{giou} \mathscr{L}_{giou}(b^{gt},\hat{b}^i)。
3.5.3 流程
使用真值框进行回归。
解码器的每个阶段对GIoU损失和L1损失进行求和。